hello LiniC,
-
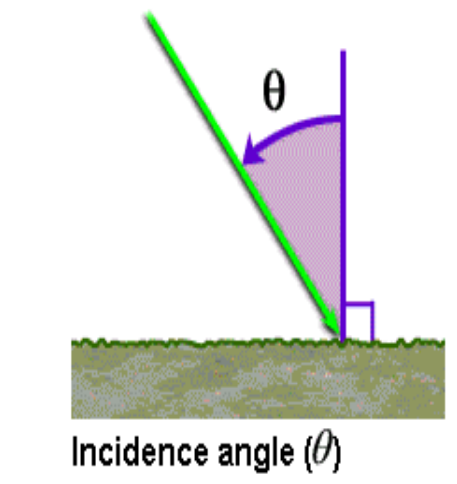
Incidence angle is the angle defined by the incident radar beam and the vertical (normal) to the intercepting surface as shown below.
-
In terms of vertical displacement, as it is given by Z.Lu and D.Dzurisin, 2014 is as follows:
Let’s say we have two pixels, m and n which corresponds to two targets on the ground, the SAR phase for these points can be defined as follows:
phase_m = (-4pi/wavelength)*rm and phase_n = (-4pi/wavelength)*rn (where rn and rm are the distance between the satellite and the points on the ground.)
A second SAR image is acquired for the same area (let’s assume that the target point n has moved up by an amount of h). Now the phase for the point n’ which has moved can be expressed as follows:
phase_n’ = (-4pi/wavelength)(rn - hcos*theta) (where h is the vertical displacement of target n)
Hence, we form the interferogram by subtracting the phases of the two SAR images and the vertical displacement between the two points can be expressed as follows:
phase_n’ = (-4pi / wavelength)(hcos*theta)
So, in order to find the vertical displacement, we need to get the cos of the incidence angle